Regenerative Aquaculture
Feature
Regenerative
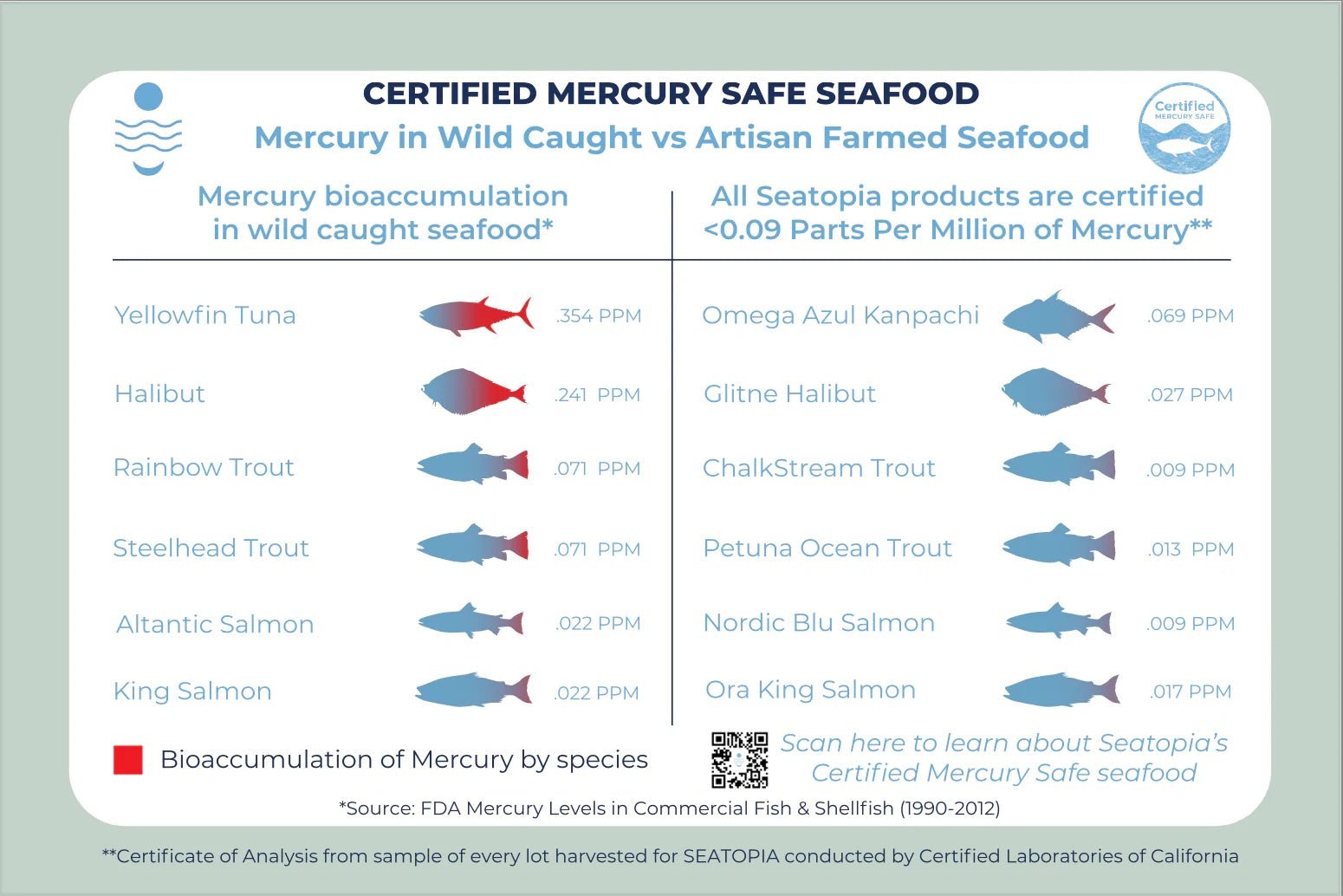
Mercury contamination in seafood is a significant concern, particularly for pregnant women and children. The FDA's reference dose for mercury helps protect these vulnerable groups by setting safe consumption limits. For example, a 150-pound pregnant woman should limit her intake of Big Eye Tuna to approximately 0.132 ounces per day due to its high mercury content. This blog post explains the calculations and offers guidance on choosing low-mercury seafood options to maintain a healthy and safe diet.
The Pristine Perception of Alaskan Waters and the Hidden Threat of Microplastics
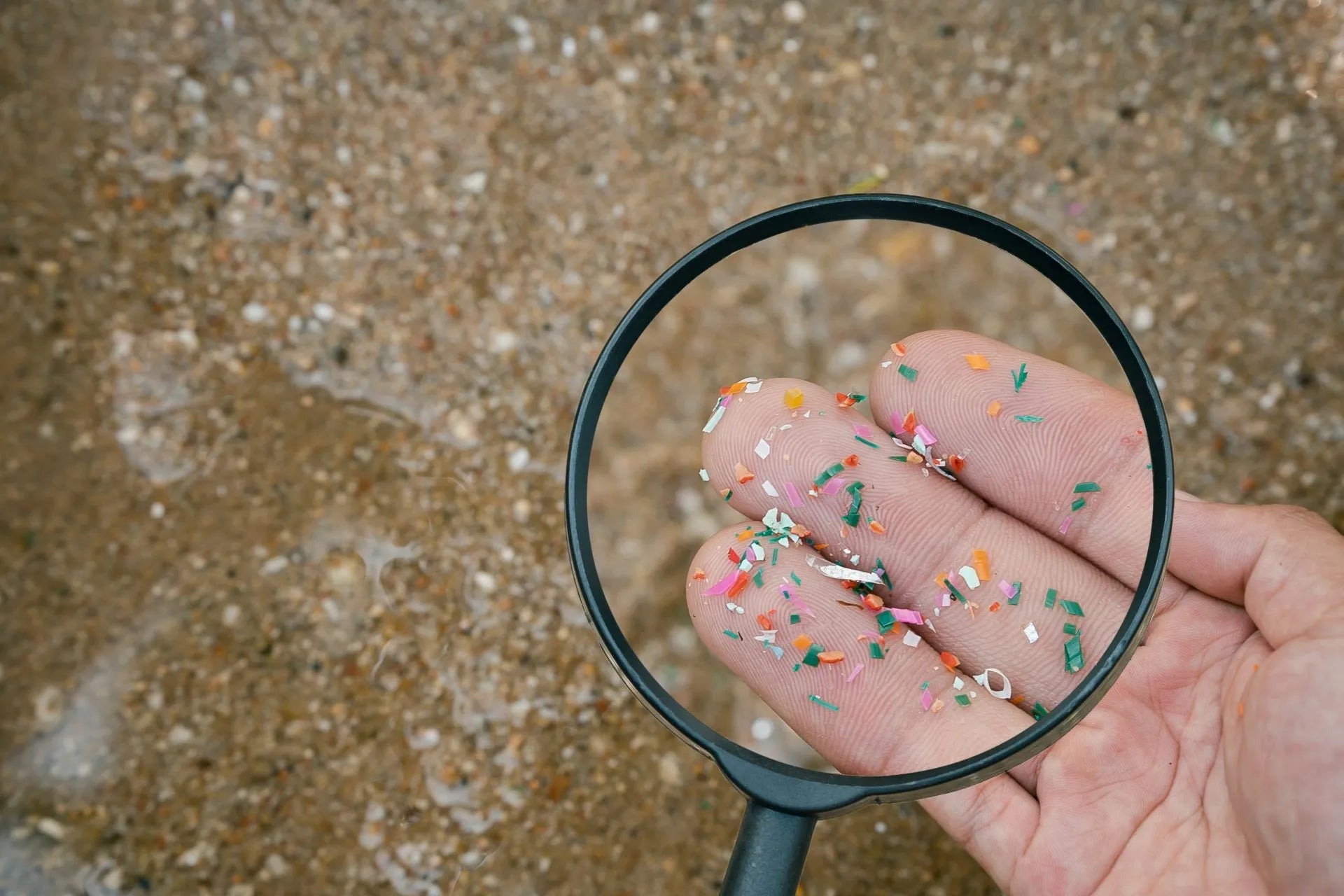
New report reveals that 100% of tested water bodies in Southcentral Alaska contain microplastics, challenging the perception of pristine Alaskan waters. Discover the hidden threats of microplastic pollution on wildlife and human health, and learn how Seatopia is leading the charge with sustainable, clean seafood practices.
Navigating Mercury in Seafood: FDA's New Survey and Seatopia's Commitment to Safe, Healthy Seafood
FDA seeks to better understand mercury levels in seafood as increasing levels of mercury in wild caught seafood can have serious health implications, especially for the developing nervous systems of babies and young children
Beyond "Wild-Caught": What You Need to Know About Seafood Safety
Are you relying solely on FDA and EPA guidelines to choose your seafood? Dive deeper into what these agencies aren't telling you about the hidden risks of mercury exposure, outdated advice, and misleading labels. Get the facts and make empowered choices with Seatopia's rigorously tested, sustainable seafood.